Yu-Ren Lin

| Name | Yu-Ren Lin |
|---|---|
| Title | Assistant Professor |
| Education | Ph.D., Institute of Science Education, National Kaohsiung Normal University |
| Extension | 61257 |
| linyuren@mx.nthu.edu.tw | |
| Office | Room 751 |
| Research Expertise | science education, scientific argumentation, nature of science, integration of games into science teaching, scientific maker education |
| Research Interests | scientific argumentation, nature of science, scientific language interaction, integration of technology into science education, teacher training, online education platform development, etc. |
| Class | Schedule 1142 |
| Experience | •Assistant professor, Institute of Mathematics and Science Education, National Tsinghua University (2022.2–present) •Associate professor, Department of Science Education and Communication, Central China Normal University (2020–2021) •Assistant professor, Department of Science Education and Communication, Central China Normal University (2016–2020) |
Teaching and Research Features
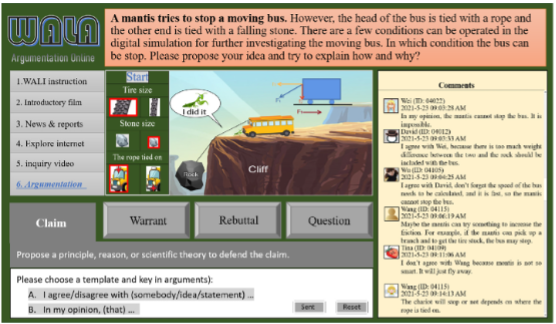
Online argumentation learning
Our research team designed an online argumentation learning process to encourage students to learn new knowledge through self-exploration and collaboration. The process includes the following steps: Posing Questions: Students first identify topics or questions of interest, which are usually open-ended with no definitive answers. Conducting Research: Students use online resources, electronic libraries, academic databases, and other tools to collect relevant information and data. Analysis and Evaluation: Students analyze the collected data, discerning the reliability and relevance of the information. Sharing and Argumentation: Students share their findings with classmates and teachers through online platforms, receive feedback, and further argumentation their learning discoveries.
Heterogeneous grouping and science inquiry
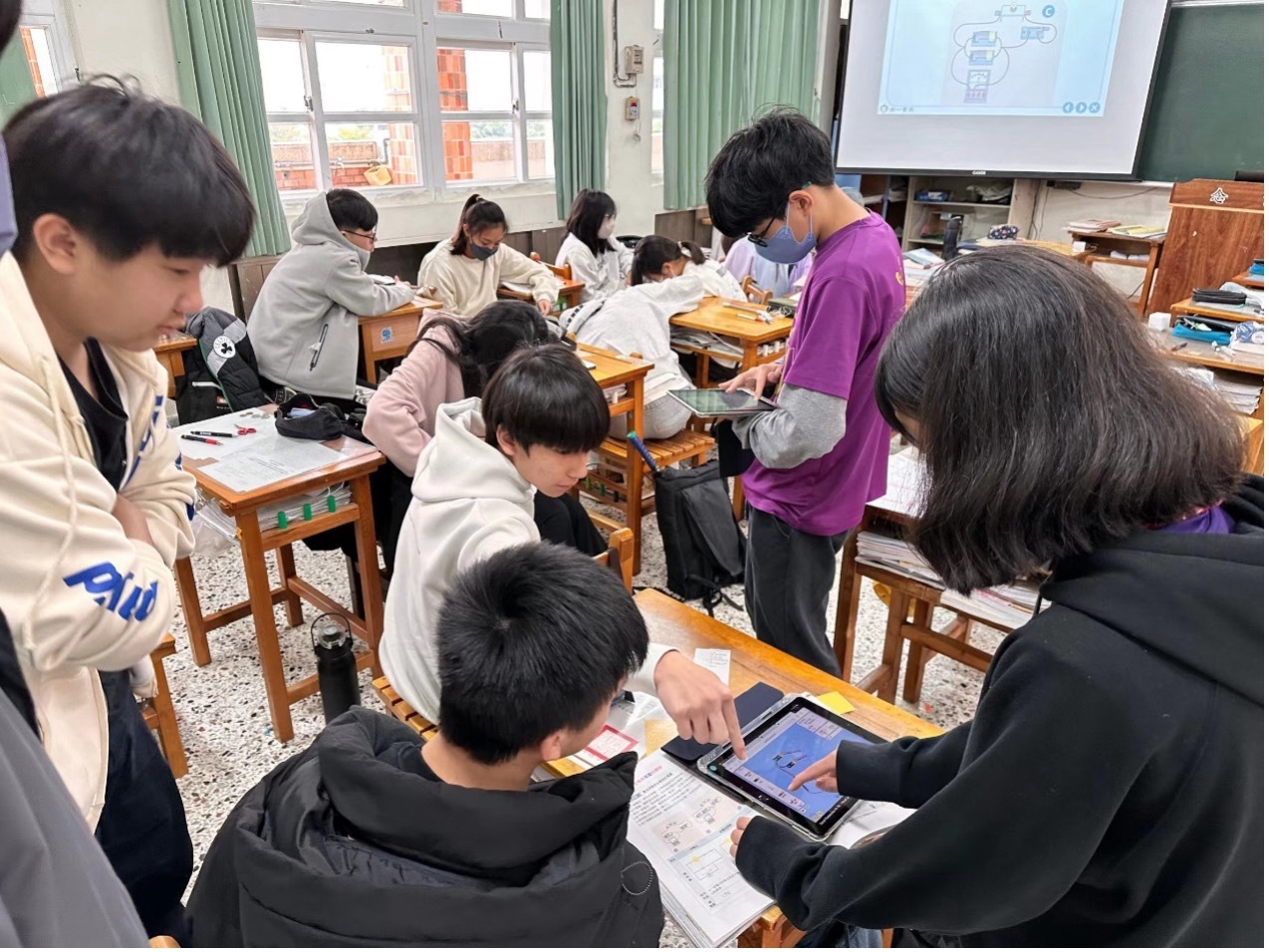

Heterogeneous grouping refers to placing students with different abilities and
backgrounds in the same group to promote collaborative learning and mutual
exchange. In such groupings, high-ability students can assist low-ability students,
enhancing each other‘s understanding, while students from diverse backgrounds can bring various perspectives, aiding in the comprehensive analysis and resolution of problems. This type of activity design effectively enhances students' learning outcomes and scientific literacy.
Game-based learning
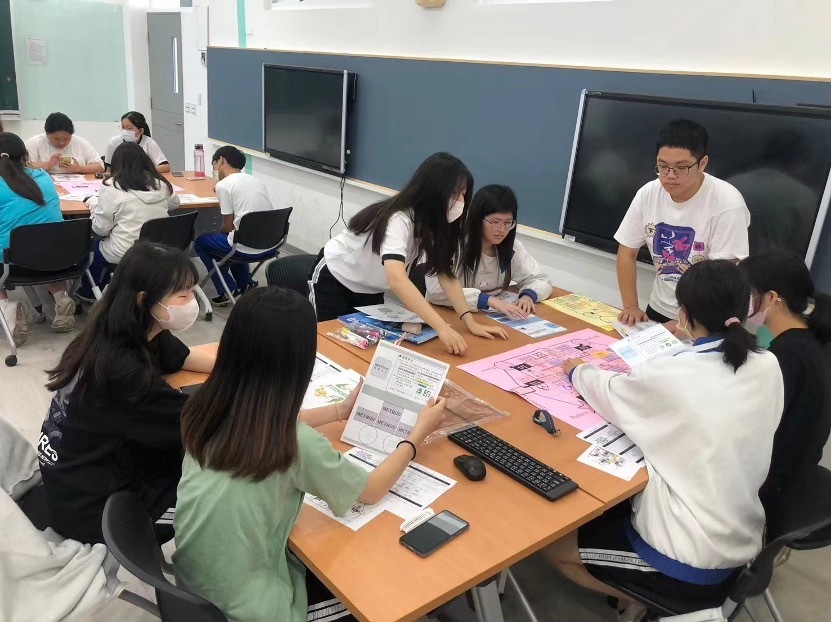

Our team also integrated science education with game-based learning, allowing students to acquire new knowledge and skills in an interactive and engaging environment. This method not only promotes critical thinking and problem-solving abilities but also fosters collaboration and communication skills. The combination of science education and game-based learning provides students with a dynamic and immersive learning experience, making the learning process more engaging and effective.
Academic Publications and Research Projects
- Lin, Y. R., & Hung, C. Y. (2025). The Synergistic Effects in an AI-Supported Online Scientific Argumentation Learning Environment. Computers & Education, 105251. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2025.105251. (If=8.9, Rank=3/760, Q1) (SSCI)
- Lin, Y. R & Wei, T. T. (2024). The effects of students’ standpoints in argumentation regarding socio-scientific issues. Journal of Baltic Science Education, 23(1), 104-118. https://doi.org/10.33225/jbse/24.23.10. (If=1.2, Rank=398/760, Q3) (SSCI)
- Lin, Y. R. (2023). An idiom-driven learning strategy to improve low achievers’ science comprehension, motivation, and argumentation. Computers & Education, CAE_104710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104710. (If=11.18, Rank=3/264, Q1) (SSCI)
- Richard, W. A., & Lin, Y. R*. (2023). Bilingual parenting: A personal narrative story of foreign bride in Taiwan towards Taiwanese-Indonesian student academic achievement and science learning. Journal of Education and Practice, 14 (35). DOI: 10.7176/JEP/14-35-03.
- Lin, Y.-R. (2022). The influence of students’ position on argumentation learning through online and face-to-face environments. International Journal of Science Education, 44(17), 2632-2657. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2022.2141082 (If=2.2, Rank=169/760, Q1) (SSCI)
- Lin, Y. R*., Fan, B., & Xie, K. (2020). The influence of web-based learning environment on low achievers' science argumentation. Computers & Education, 151. (If=8.53, Rank=3/264, Q1) (SSCI)
- Lin, Y. R.* (2019). Student positions and web-based argumentation with the support of the six thinking hats. Computers & Education, 139, 191-206. (If=8.53, Rank=3/264, Q1) (SSCI)
- Liu, Q. T., Liu, B. W., & Lin, Y. R.* (2018). The influence of prior knowledge and collaborative online learning environment on students’ argumentation in descriptive and theoretical scientific concept, International Journal of Science Education, 41, 165-187. (If=3.20, Rank=102/235, Q2) (SSCI)
- Lin, Y. R.* (2018). The influences of contextualized media on students' science attitudes, knowledge, and argumentation learning through online game‐based activities. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 34, 884-898. (If=3.86, Rank=30/237, Q1) (SSCI)
- Lin, Y. R.*, Hung, C. Y. & Hung, J. F. (2017). Exploring teachers’ meta-strategic knowledge of science argumentation teaching with the repertory grid technique. International Journal of Science Education, 39, 105-134. (If=3.20, Rank=102/235, Q2) (SSCI).
- Hung, C. Y., Lin, Y. R., Huang, K. Y., Yu, P. T., & Sun, J. C. Y. (2017). Collaborative game-based learning with motion-sensing technology: Analyzing students’ motivation, attention, and relaxation levels. International Journal of Online Pedagogy and Course Design, 7(4), 53-64. (If=0.450, Rank=482/723, Q3)
- Weng, W. Y., Lin, Y. R., She, H. C. (2017). Scaffolding for argumentation in hypothetical and theoretical biology concepts. International Journal of Science Education, 39(7), 877-897. (If=3.20, Rank=102/235 , Q2) (SSCI).
- Lin, Y. R.*, & Hung, J. F. (2016). The Analysis and Reconciliation of Students’ Rebuttal in Argumentation Activities. International Journal of Science Education, 38, 130-155. (If=3.20, Rank=102/235 , Q2) (SSCI)
- Chia-Hung Kuo & Yu-Ren Lin*(2025 accepted). Enhancing Students’ Science Learning Through an Idiom-Integrated Instructional Approach: Effects on Motivation, Conceptual Understanding, and Argumentation. The 6th International Conference on Modern Man-agement based on Big Data (MMBD2025), 2025, Hong Kong.
- Yu-Ren, Lin (2024, Feb). Science Argumentation in Online Game-based Environment. World Conference on Education and Training, WCET 2024, Singapore., Singapore.
- Bin, Fan,. & Yu-Ren, Lin* (2021). The construction of web-based scaffoldings for low achievers’ science inquiry and argumentation learning. Global Chinese Conference on Computers in Education, GCCCE 2021, Hong Kong, Taipei & Beijing.
| 計畫編號 | 計畫名稱 | 計畫期間 | 擔任工作 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| • | 專題研究計畫: 113-2410-H-007 -013 - | 台灣本土社會性科學議題論證平台建設與學生品格培養之研究 | 2024/08/01- 2025/07/31 | 主持人 |
| • | 專題研究計畫: 112-2410-H-007 -017 - | 本土文化融入科學論證線上學習平台設計與推廣 | 2023/08/01- 2024/07/31 | 主持人 |
| • | 新進人員研究計畫: 111-2410-H-007 -031 - | 科學論證心智模型的探索與推廣-論證知識的衝突與再建構 | 2022/06/01- 2023/05/31 | 主持人 |